|
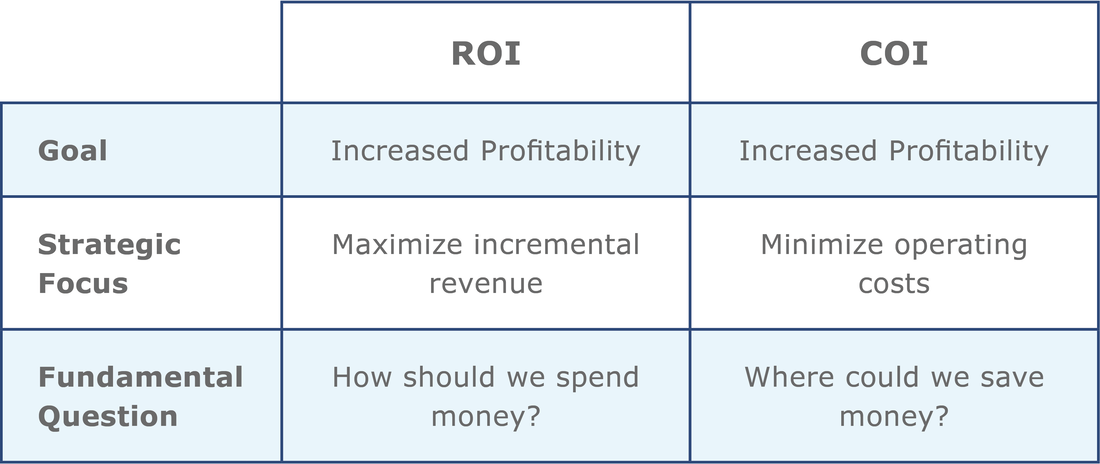
Technology and fleet vehicles are being updated and security is improving. Nevertheless, the number of accidents remains unchanged. Rising costs of road accidents means bad news for fleet companies. Proper management and proactive dedication to improving safety can significantly impact the overall costs of fleet accidents. Safety measures are not a one-time event. Security systems must be constantly updated. The responsibility of the fleet managers is to take care of the continuous improvement of safety measures, or they can encounter the consequences of the so-called cost of ignore (COI) program. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN FINANCIAL AND BUSINESS STRATEGIES - COI and ROI The definition of Cost of Ignoring or COI is the additional expense or lost savings that results when a company fails to make a strategic business investment that might improve operational efficiency, or in this case safety. In other words, for fleet managers, it can be thought of as the incremental operating costs resulting from the improper use of telematics (or in some cases the complete lack of telematics). Although COI has the same strategic objective as its better-known cousin Return on Investment (ROI), there are a few fundamental differences, as captured in the table below. In summary, COI is focused on minimizing operating costs, whereas ROI is focused on maximizing incremental revenue. To sum up, the cost of ignoring will bring temporary positive financial results, but with the risk of higher costs that will result from technical and program failures, accidents, insurance, etc. 4 METHODS OF A PROTECTIVE SECURITY MEASURES There are four specific areas where we can find savings: safety, fuel, maintenance and productivity. 1. SAFETY (reducing the number of traffic accidents): Each work-related disaster costs the company from 10,000€ to 500,000€ depending on the severity of the accident. Insurance companies have provided information that in vehicles that use telematics, the number of accidents and costs is reduced by as much as 50%. 2. FUEL (controlling fuel consumption according to driving mode): The US Department of Energy reports that rapid acceleration and braking may increase fuel consumption by up to 33% when driving on the highway and 5% on urban roads. Combined with effective driver training initiatives to reduce aggressive driving and telematics, fuel costs can be reduced to 14%. 3. MAINTENANCE (Reduced repairs and maintenance): scheduled maintenance is a standard part of vehicle ownership, but unplanned repairs due to aggressive driving and vehicle misuse fall under the category of unnecessary costs. Costs due to less planned maintenance services range from EUR 400 to EUR 700 per day. Telematics technology helps the company reduce both planned and unplanned repair and maintenance of vehicles up to 14%. 4. PRODUCTIVITY (Increased labor force efficiency): Driver compensation is often a major component of the overall operational fleet budget. Market research suggests that telematics can increase labor productivity and reduce labor costs by up to 12%. Telematics significantly contributes to a better financial plan and improve the safety of fleet vehicles. The best technology on the Slovenian market, which proactively improves fleet management and realizes the savings described above, is GEOTAB. By clicking on the word GEOTAB, you can read the product's details and order your very own Geotab telematics.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

